Label-free quantification of cell growth and morphology using artificial intelligence and advanced data analytics
Live-cell imaging enables scientists and researchers to acquire phase contrast images and provides an ideal platform to study complex biological models. As these models move towards using more relevant and precious cell types, it becomes even more important to use label-free, non-perturbing analysis methods.
This webinar explores how incorporating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data-science based algorithms into user-friendly workflows allows quantification of a wide range of cellular models.
More information
Live-cell imaging enables acquisition of phase contrast images and provides an ideal platform to study multifaceted biological paradigms in drug discovery. The movement of these models towards increasingly complex ones, using more relevant and precious cell types, has highlighted the importance of label-free analysis methods that are non-perturbing. Incorporating Artificial Intelligence (AI), and data-science based algorithms, into user-friendly workflows has enabled powerful quantification of a wide range of cellular models.
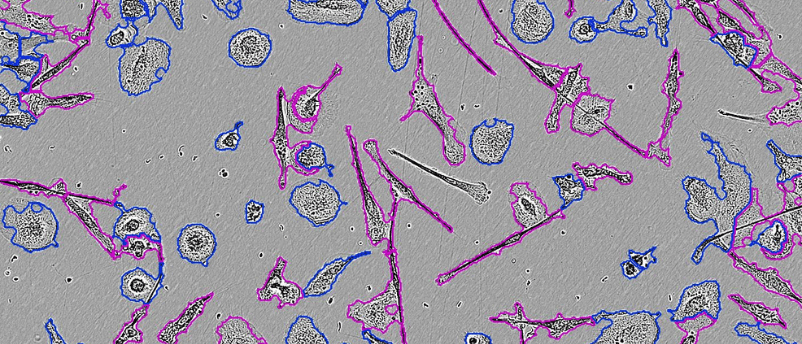
We demonstrate an automated, robust solution for label-free cell segmentation using integrated AI-based software. The Incucyte® AI Confluence analysis, driven by a pre-trained convolutional neural network (CNN), allows us to reliably monitor cell proliferation in a non-perturbing unbiased manner with minimal user input. In this webinar, we show validation of accurate segmentation across cell types with different morphologies.
Analysis of cell morphology is a powerful technique that can provide insight into cell viability and behaviour. The Incucyte® Advanced Label-Free Classification Software Module uses sophisticated multivariate analysis to monitor two user-defined populations based on multiple aspects of cell shape. We demonstrate the application of this simplified workflow to biological models that undergo morphological changes, including a Live/Dead and differentiation assay.
We also exemplify how AI Confluence or Advanced Label-fee Classification can provide high-throughput physiologically relevant insight into cell heath and be utilized for the investigation of compound efficacy in drug discovery.
Overall, live-cell imaging and intuitive label-free analysis is a powerful approach that provides objective, meaningful quantitative analysis of complex biological behaviour.
What will you learn?
-
-
- How an integrated AI-driven approach provides accurate measurements of proliferation across a range of cell types
- Demonstration of a simplified workflow using Advanced Label-free Classification for the quantitative analysis of diverse changes in cell morphology
- Validation of label-free analysis methods for robustly quantifying cell health in a non-perturbing manner
- Guidance on how live-cell imaging and intuitive label-free analysis can be built into your development workflow
-
Who may this interest?
Scientists and researchers in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, biopharma, and academia.
Speaker

Jasmine Trigg
Scientist
Sartorius
Jasmine is currently a Scientist at Sartorius as part of the Cell Imaging and Applications group within the Bio Analytics team, where she is involved in the research and development of novel applications for the Incucyte® Live-Cell Analysis Systems.
Over the past couple of years, she has worked across multiple research areas developing cellular assays to extend the suite of live-cell analysis applications. Jasmine has a background in neuroscience and genetic manipulation and her earlier work focused on using a combined structural and molecular biology approach to assess disease-associated proteins implicated in Alzheimer’s disease.
This webinar was recorded on Wednesday 18th May 2022
